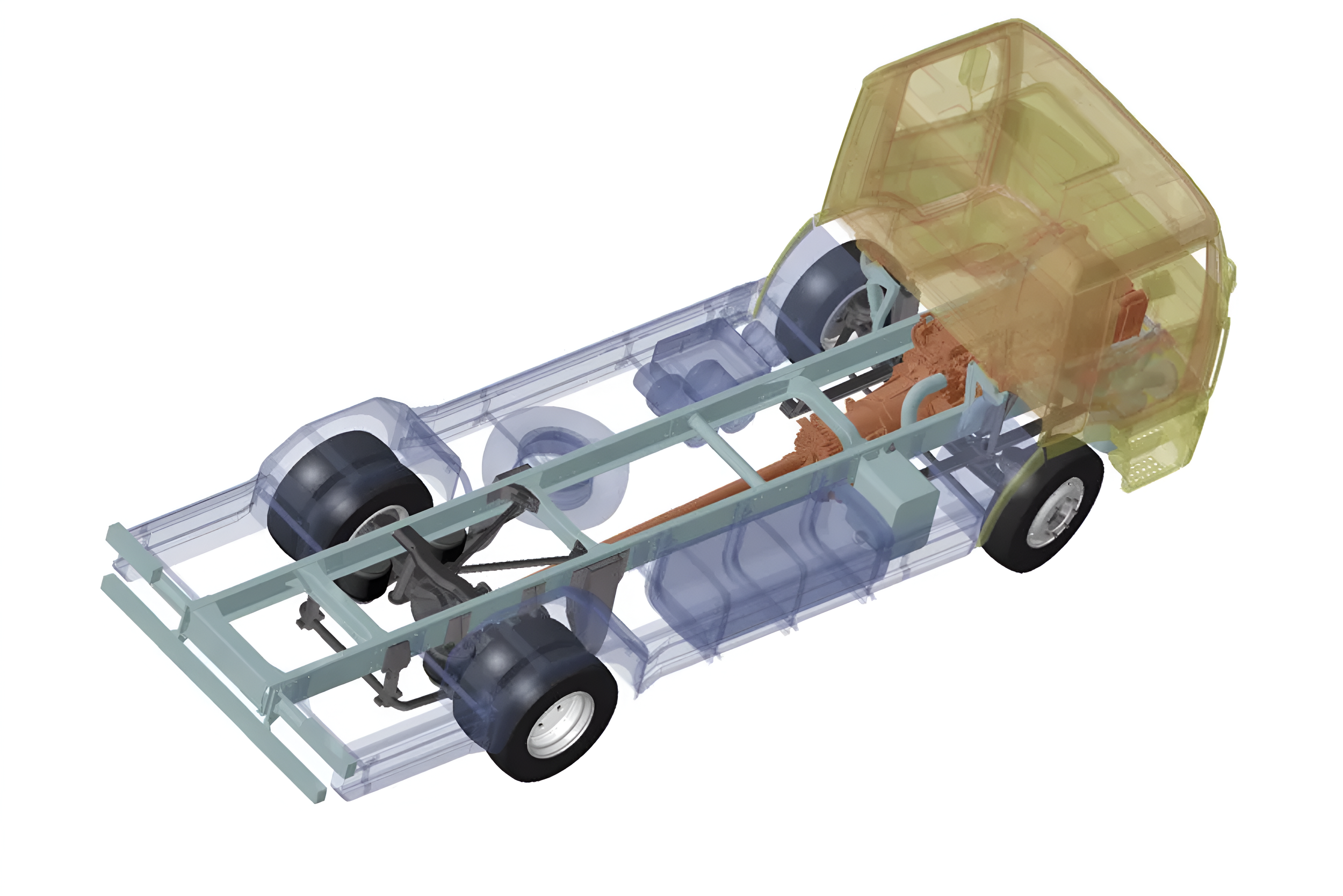
Powertrain by Mega EV
Powertrain: Definition & Components
The powertrain refers to the core mechanical systems in a vehicle that generate and deliver power to propel it across land, water, or air. It typically includes the engine, transmission, driveshafts, differentials, and final drive components—such as drive wheels, continuous tracks (as seen in military tanks or construction equipment), or propellers for marine and aviation applications.
In some contexts, the term "powertrain" may refer more narrowly to just the engine and transmission, especially when other components are not directly integrated into the transmission system.
Driveline / Drivetrain
The driveline, also known as the drivetrain, consists of the elements of the powertrain excluding the engine and transmission. It includes the systems that transmit power from the transmission to the wheels or other propulsion mechanisms. The specific configuration of the driveline varies based on the vehicle’s drive layout, such as:
Front-Wheel Drive (FWD)
Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD)
All-Wheel Drive (AWD) / Four-Wheel Drive (4WD)
Six-Wheel or Eight-Wheel Drive (6×6 / 8×8) for specialized or military vehicles
Expanded Powertrain Concept
In a broader context, the powertrain encompasses all components involved in converting stored energy into kinetic energy for propulsion. This includes not only traditional internal combustion systems but also alternative and hybrid power sources, such as:
Electric motors & battery systems
Fuel cells (hydrogen)
Solar panels
Nuclear energy (for naval vessels or spacecraft)
Kinetic or potential energy systems
This wider interpretation also covers non-wheel-based vehicles, including aircraft, boats, and tracked vehicles—highlighting the powertrain’s role as the foundational system in all forms of mechanical propulsion.