EV Technology
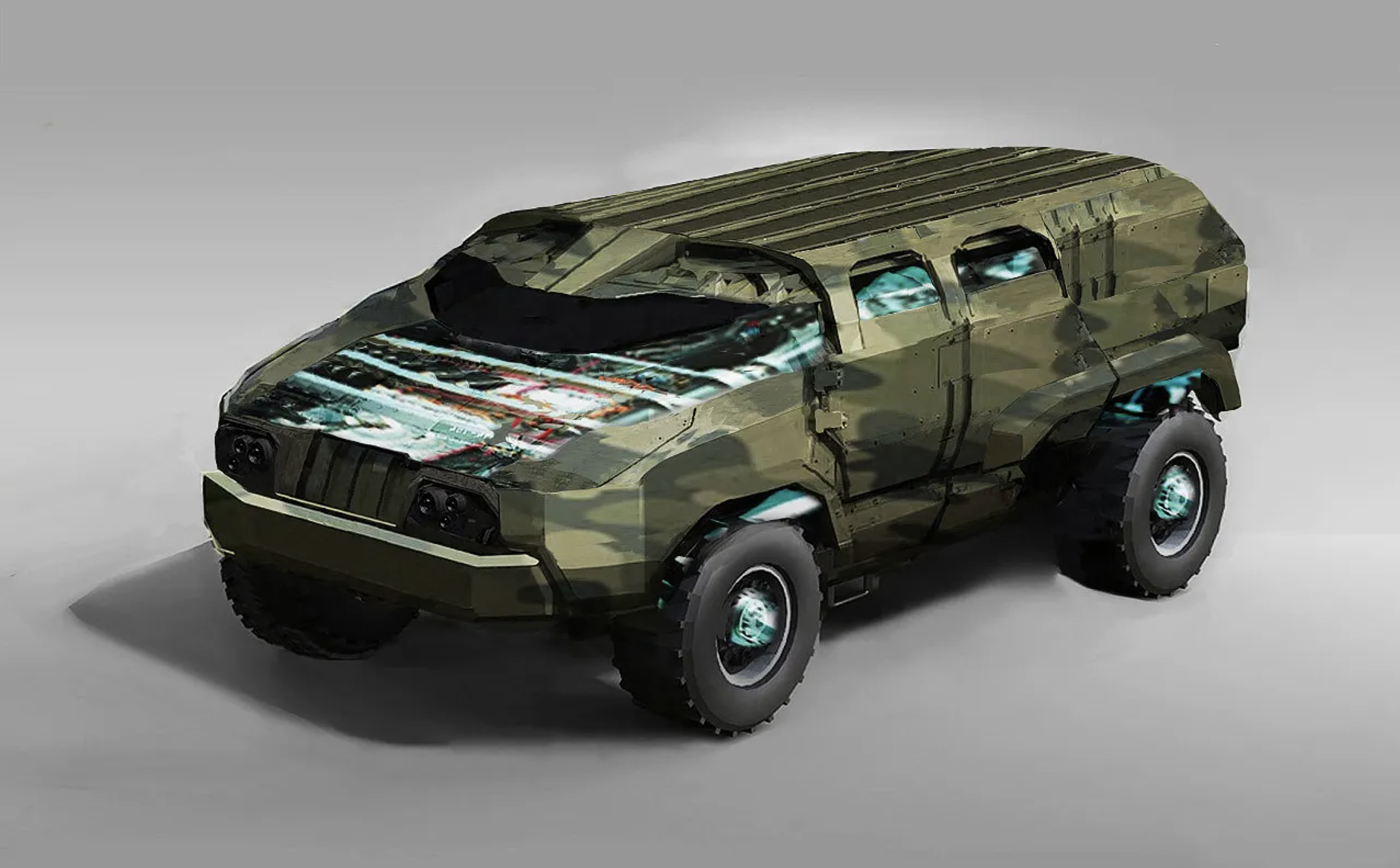
EV technology plays a crucial role in the development of Mega's military vehicles, aiming to bridge the cost gap between electric and internal combustion engine (ICE) counterparts while enhancing performance and sustainability. Historically, electric vehicles (EVs) were significantly more expensive due to the high cost of lithium-ion battery packs. However, advancements in battery technology and large-scale production have driven costs down, making EVs more viable for military applications. Mega’s military EVs leverage these innovations to provide superior mobility, stealth, and operational efficiency while reducing logistical burdens. As battery prices continue to decline, these vehicles will become even more cost-effective, ensuring a strategic advantage in modern defense operations.
-
The cost of charging an electric vehicle (EV) battery depends on electricity rates, which vary by location. For military applications, this translates to a more predictable and controlled energy cost compared to volatile fuel prices, reducing budget uncertainties and operational expenses. Historically, EVs demonstrated significant cost advantages in civilian use—for example, as of November 2012, a Nissan Leaf driving 500 miles (800 km) per week in Illinois incurred an estimated annual charging cost of $600, significantly lower than the fuel costs of a comparable gasoline-powered vehicle. Energy consumption varies by vehicle design and efficiency; the General Motors EV1 consumed approximately 11 kWh per 100 km (0.18 kWh per mile), while the 2011/12 Nissan Leaf used 21.25 kWh per 100 km (0.342 kWh per mile), according to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
For military fleets, EVs offer superior cost efficiency over time, reducing not just fuel expenses but also maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Nissan previously estimated that the Leaf's five-year operating cost in the U.S. would be around $1,800, compared to $6,000 for a gasoline-powered car. Similar cost reductions apply to military electric vehicles (EMVs), allowing defense agencies to redirect resources toward mission-critical areas rather than fuel logistics.
Another key advantage for EMVs is their energy independence. Traditional military operations rely heavily on fuel convoys, which are not only expensive but also highly vulnerable to attacks. EVs, however, can be charged from renewable energy sources such as solar-powered field stations, reducing the reliance on external fuel supplies and increasing battlefield resilience. Silent operation further enhances stealth capabilities, making EMVs ideal for reconnaissance, special forces missions, and urban warfare where noise reduction is critical.
With continuous advancements in battery technology, decreasing costs, and the adoption of renewable energy, EV charging is becoming more affordable and sustainable. As a result, electric military vehicles present a strategic and economic advantage, ensuring lower costs, greater operational flexibility, and enhanced battlefield effectiveness in modern defense operations.
4o
-
For military applications, the advantages of electric vehicles (EVs) extend beyond fuel cost savings. Electric military vehicles significantly reduce logistical dependency on fuel supply chains, a critical factor in remote and hostile environments where fuel convoys are vulnerable to attacks. Their superior energy efficiency results in lower operating costs, reducing long-term expenditures for defense budgets. Additionally, EVs offer stealth advantages due to their near-silent operation, minimizing acoustic signatures that could expose troop movements.
Moreover, the ability to integrate renewable energy sources such as solar charging stations in the field allows for greater operational flexibility and reduced reliance on traditional fuel infrastructure. With battery technology advancing rapidly, improvements in range and energy storage capacity are making electric military vehicles more viable for extended missions. These benefits, combined with the increasing affordability of EV technology, position electric-powered military fleets as a strategic and cost-effective choice for modern defense operations.
-
EV technology offers several key advantages over conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, making it particularly beneficial for military applications. Electric military vehicles (EMVs) eliminate local air pollution since they produce no tailpipe emissions, enhancing their operational suitability for urban environments, enclosed spaces, and regions with strict environmental regulations. Additionally, they contribute to a reduction in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, depending on the source of electricity used for charging. When powered by renewable energy or grid electricity with a lower carbon footprint, EMVs provide a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to fossil-fuel-powered military fleets.
Beyond environmental benefits, electric vehicles significantly improve strategic mobility and operational efficiency. Unlike gasoline vehicles, which rely on a highly carbon-intensive supply chain involving extraction, refining, and transportation, EVs streamline logistics by reducing the need for fuel convoys—one of the most vulnerable elements in military operations. Their silent operation enhances stealth capabilities, making them ideal for reconnaissance, special operations, and reducing acoustic detection in combat scenarios.
Furthermore, EMVs offer superior energy efficiency, converting a higher percentage of stored energy into propulsion compared to ICE vehicles. They also support energy resilience by integrating with battlefield microgrids, solar charging stations, and mobile power units, ensuring continued operation in remote or contested areas without reliance on traditional fuel supply lines. As battery technology advances, increasing energy density and reducing costs, electric military vehicles will play a crucial role in enhancing battlefield effectiveness, reducing costs, and supporting sustainable defense strategies for the future.
EV Technology BENEFIT
EV technology offers several key advantages over conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, making it particularly beneficial for military applications. Electric military vehicles (EMVs) eliminate local air pollution since they produce no tailpipe emissions, enhancing their operational suitability for urban environments, enclosed spaces, and regions with strict environmental regulations. Additionally, they contribute to a reduction in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, depending on the source of electricity used for charging. When powered by renewable energy or grid electricity with a lower carbon footprint, EMVs provide a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to fossil-fuel-powered military fleets.
Beyond environmental benefits, electric vehicles significantly improve strategic mobility and operational efficiency. Unlike gasoline vehicles, which rely on a highly carbon-intensive supply chain involving extraction, refining, and transportation, EVs streamline logistics by reducing the need for fuel convoys—one of the most vulnerable elements in military operations. Their silent operation enhances stealth capabilities, making them ideal for reconnaissance, special operations, and reducing acoustic detection in combat scenarios.
Furthermore, EMVs offer superior energy efficiency, converting a higher percentage of stored energy into propulsion compared to ICE vehicles. They also support energy resilience by integrating with battlefield microgrids, solar charging stations, and mobile power units, ensuring continued operation in remote or contested areas without reliance on traditional fuel supply lines. As battery technology advances, increasing energy density and reducing costs, electric military vehicles will play a crucial role in enhancing battlefield effectiveness, reducing costs, and supporting sustainable defense strategies for the future.
ELECTRIC AMBULANCE
ELECTRIC TAXI
ELECTIFYING FLEET
ELECTRIC WASTE TRUCK
ELECTRIC POSTAL TRUCK
ELECTRIC SHERIFF VEHICLE
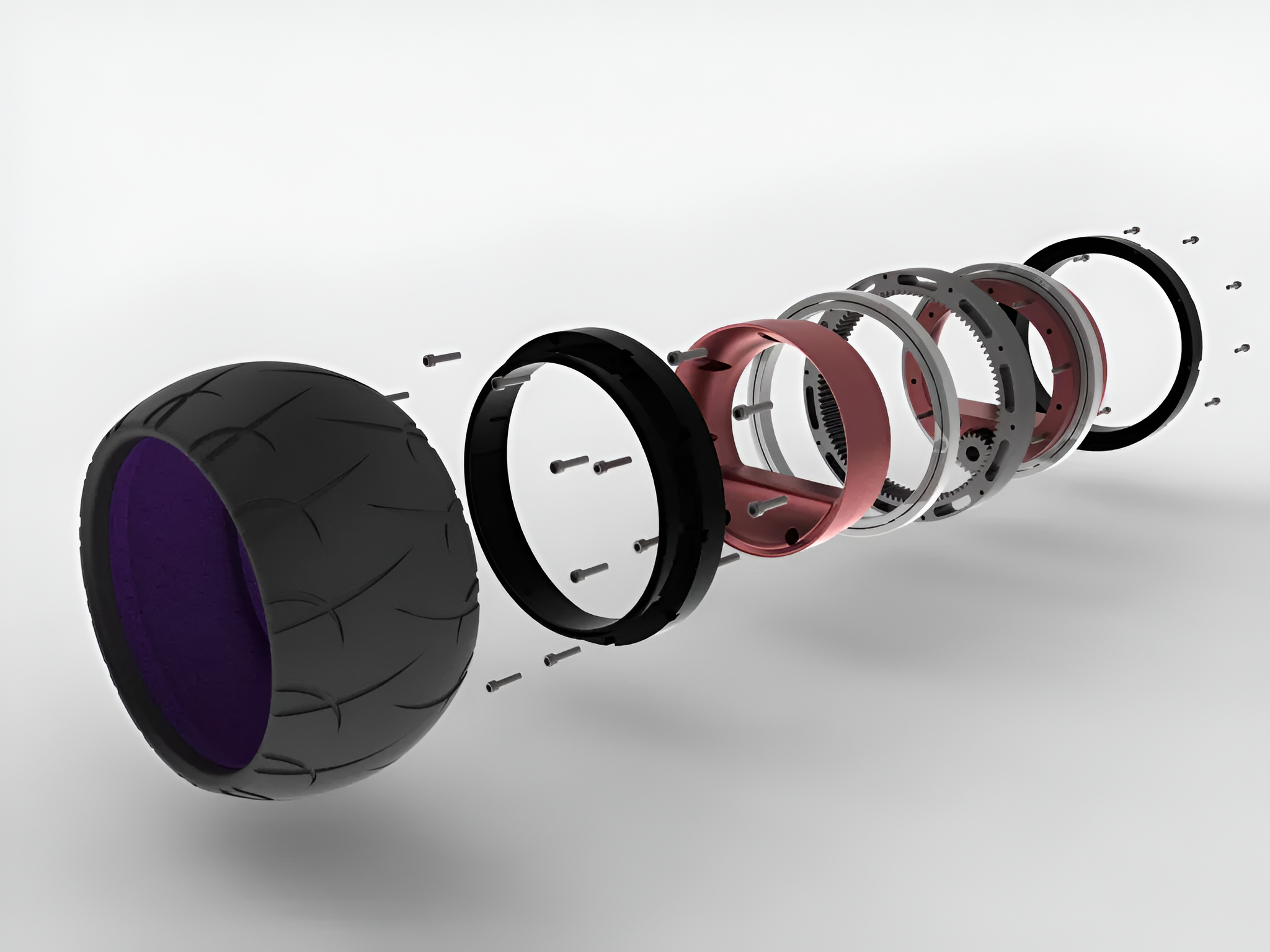
MEGA: Research and Development in Advanced Electric In-Wheel Motor Systems
At MEGA, our R&D in next-generation electric in-wheel motor systems is redefining vehicle propulsion by eliminating traditional drivetrains and central powertrains. By embedding high-performance motors directly into the wheels, we achieve unmatched power delivery, vehicle agility, and modular design flexibility—crucial for military, commercial, and extreme-terrain applications.
Our work focuses on maximizing power density, thermal efficiency, and durability through innovations in advanced cooling systems, ultralight composite materials, and integrated regenerative braking. MEGA is also pioneering AI-driven motor control algorithms and high-voltage, solid-state power architectures to boost real-time energy optimization and extend operational range.
With in-wheel motors, MEGA enhances the stealth, maneuverability, and survivability of platforms like the Stealth Raptor, enabling true all-wheel-drive dynamics, independent torque vectoring, and improved ground clearance—transforming the future of electric mobility across defense and high-performance sectors.
We can make a difference, together












